

Note: for bent molecular geometry when the electron-pair geometry is trigonal planar the bond angle is slightly less than 120 degrees, around 118 degrees. VSEPR Theory: a chemistry model used to predict the shape of individual molecules based on electron-pair electrostatic repulsion The best guide to the covalent or ionic character of a bond is to consider the types of atoms involved and their relative positions in the periodic table. The table below summarizes the molecular and electron-pair geometries for different combinations of bonding groups and nonbonding pairs of electrons on the central atom.The main geometries without lone pair electrons are: linear, trigonal, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral. Most molecular geometry can be explained by counting the valence electrons in a molecule and accounting for how they want to be as far away from each other as possible.It has one atom at the center and three at the corners of an equilateral triangle, making a. Hence, atoms in the third row of the periodic table can follow the octet. Trigonal Planar: The molecule forms a triangular shape in one plane. Determining molecular geometry and bond angles To determine the molecular geometry of a structure we need to know two things. Below is a table demonstrating the relationship between the number of bonding partners and these configurations.
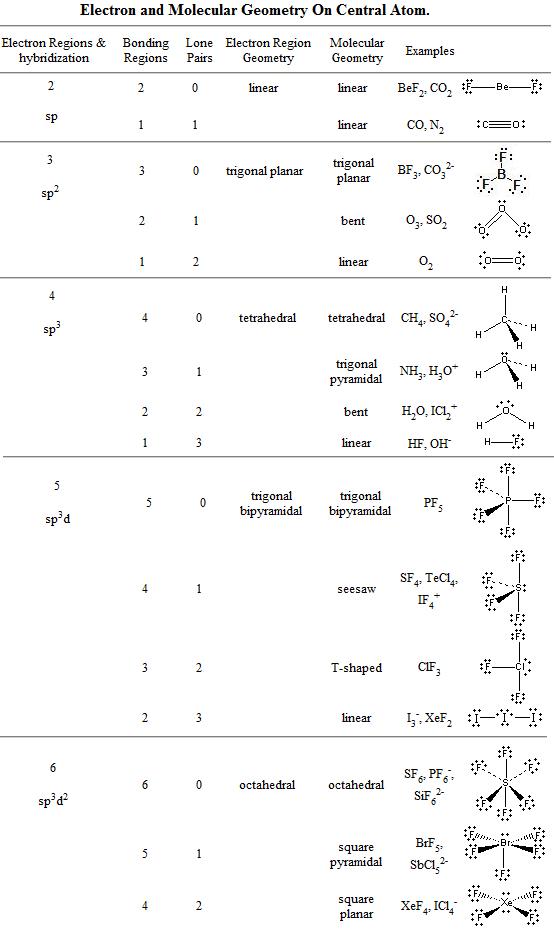
However, since the 3s and 3p orbitals are lower energy than the 3d orbitals, electrons tend to occupy the s and p orbitals first. There are three main types of configurations: linear, trigonal, and tetrahedral. The number of valence electrons in the central atom must be determined.

If we combine the splitting schemes for the 2s and 2p orbitals, we can predict bond order in all of the diatomic molecules and ions composed of elements in the first complete row of the periodic table. However, when constructing the periodic table in Unit 4, we saw that the third shell has one s orbital, three p orbitals, and five d orbitals. Determination of Electron Geometry Predict the molecules central atom. Molecular geometries take into account the number of atoms and the number of lone pair electrons. Learning Objectives To apply Molecular Orbital Theory to the diatomic homonuclear molecule from the elements in the second period.Fundamentally, the VSEPR model theorizes that regions of negative electric charge will repel each other, causing them (and the chemical bonds that they form) to stay as far apart as possible. Constructing Models in Teaching of Chemical Bonds: Ionic Bond, Covalent Bond, Double and Triple Bonds, Hydrogen Bond and Molecular Geometry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
